Microarray chip refers to the method of in-situ synthesis or micro-spotting of light guides to sequentially solidify a large number of biological macromolecules such as nucleic acid fragments, polypeptide molecules or even tissue sections, cells and other biological samples on supports (such as slides and nylon membranes). The surface of the carrier, consisting of a dense two-dimensional molecular arrangement, and then reacting with the target molecule in the labeled biological sample to be tested, and the intensity of the reaction signal is detected rapidly, in parallel, and efficiently by a specific instrument such as a laser scanner. To determine the number of target molecules in the sample.

Microarray chips are characterized by high density arrays. The basic research began in the late 1980s and is essentially a biotechnology developed primarily in the field of biogenetics.
Microarrays are divided into cDNA microarrays and oligonucleotide microarrays. The microarray has a large number of DNA probes with known partial sequences. The microarray technology uses the principle of molecular hybridization to hybridize the simultaneously compared specimens (labeled with isotopes or fluorescein) to the microarray to detect the hybridization signal intensity. And data processing, transforming them into the abundance of specific genes in different specimens, so as to comprehensively compare the differences in gene expression levels of different specimens. Microarray technology is a powerful tool for exploring genomic functions.
The microarray chips are classified according to the probes on the chip. There are nucleic acid chips, protein chips and tissue chips. The most widely used nucleic acid chips are nucleic acid chips. There are two types of nucleic acid chips, namely cDNA microarrays and oligonucleosides. Acid microarray.
Microarray chips are mainly used for expression analysis, genotyping and sequencing; analysis or optimization of protein-protein interactions; screening of proteomes for antibody recognition; for pathological studies; for screening large compounds and genomic libraries And systematically study the microenvironment of local cells; the ability to identify and evaluate small molecules, so it appears to be more useful than other technologies in the pharmaceutical industry. Also used in functional genomics research and toxicology experiments, biomarker research, etc.
The Azure Sapphire dual-mode multispectral laser imaging system features the following :
- Dual mode imaging: dual mode with scan detection and CCD imaging
- 4 solid-state laser laser excitation: 488nm (blue), 520nm (green), 658nm (red), 785nm (NIR), giving users more fluorescence options
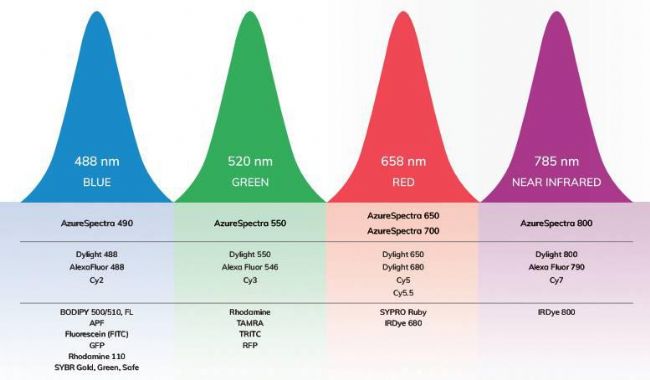
- The only three detector designs: PMT, APDs and CCD detectors, PMT detector for blue fluorescence detection and phosphor screen imaging; 3 independent APD detectors for green, red fluorescence detection and dual near-infrared fluorescence detection, high Resolution CCD for highly sensitive chemiluminescence detection

- Scanning method: 4 channels simultaneous scanning, faster scanning
- Higher resolution: up to 10 micron resolution for sharper imaging
- Broader dynamic range: Simultaneous quantification of low-abundance proteins and high-abundance proteins for more accurate quantification
- Use confocal optical path: reduce background noise, higher signal to noise ratio

The Azure sapphire dual-mode multispectral laser imaging system enables ultra-high resolution and up to 4 laser excitation sources to assist microarray research, enabling rapid, parallel, and efficient detection and analysis to determine the number of target molecules in a sample.
Endotracheal Tube,tube endotracheal,endotracheal tube holder,oral endotracheal tube,endotracheal tube price
Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.jssinoanesthesias.com